Difficult molecular replacement problems (e.g. homology less than 30%) can be helped by trimming loops and side chains from the target model where it has poor sequence alignment to the search sequence. To run this task you can enter either the search sequence for which the task will perform an alignment to the template structure or you may import your preferred alignment. You may get a better alignment of the template and target sequence from tools such as HHPred, PROMALS3D or FFAS. The supported sequence and alignment formats are described in the Model data documentation.
Input
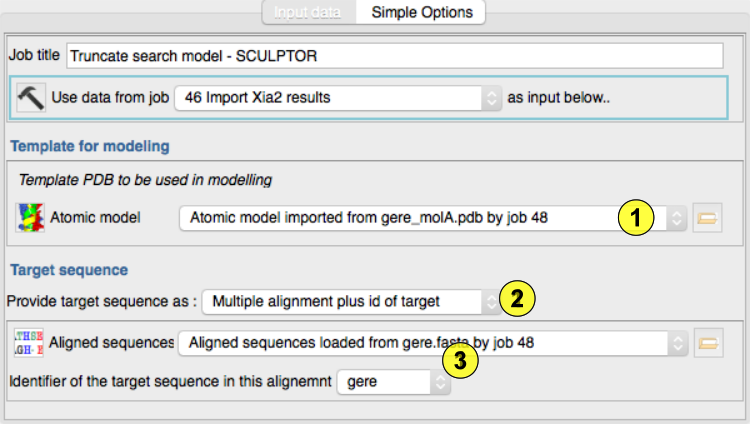
Select the template structure(1)
Choose to enter the target sequence or an alignment(2)
Select and alignment file and specify which sequence in the file is the target.(3)
Options
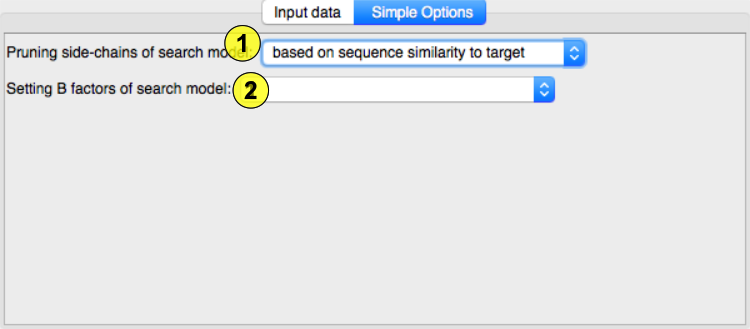
(1)Pruning side chain alternative modes (from Phenix documentation): schwarzenbacher Implements the algorithm published by Schwarzenbacher et al. (2004), who propose that for optimal molecular replacement results a residue sidechain should be truncated if aligned with a non-identical residue, and not truncated otherwise. The level of truncation is controlled by the pruning_level parameter, and defaults to 3 (which corresponds to Cgamma) and can be controlled by the pruning_level parameter of the schwarzenbacher scope. Similarity Uses sequence similarity values for deciding the level of truncation. Residues above full_truncation_limit are not truncated at all, those below the full_truncation_limit are truncated to Cbeta, and those in between are truncated according to the pruning_level parameter (all available from the similarity scopei). Results tend to be similar to those given by the Schwarzenbacher algorithm; however, it is possible to get high similarity values (and full sidechain preservation) for certain substitutions (i.e. TYR to PHE), and low-sequence similarity zones can end up being truncated to Cbeta.
(2)B factor of model: original This uses the original B-factor of atoms. This is primarily intended as a contributor to a combination, but can also be used to manipulate current B-factors, e.g. set them to a constant value. asa This calculates accessible surface area for an isolated chain and transforms the raw values to B-factors. A high ASA-value indicates a potential for flexibility. The calculation can be configured by the precision and probe_radius parameters of the asa scope. similarity Low sequence similarity regions tend to be more dissimilar.
INSERT TEXT HERE