Molecular replacement results are generally improved if the search model is pruned to remove side chains which are not conserved between the search model and the target structure. This task takes an alignment between target and model sequences and modifies the model pdb file by renaming and pruning non-conserved residues. The names of the retained atoms will be changed if necessary to match the target. Conserved residues are left unchanged.
The residues in the output pdb file will be numbered in a way consistent with the target sequence i.e. if a residue in the target corresponds to a gap in the model, the residue numbers in the output pdb file will contain a gap, but if a residue in the model corresponds to a gap in the target, the residue numbers in the output pdb file will be consecutive.
If there are alternate conformations in the input pdb file, chainsaw will choose the most probable conformation, and assign it an occupancy of 1 in the output pdb file.
Input
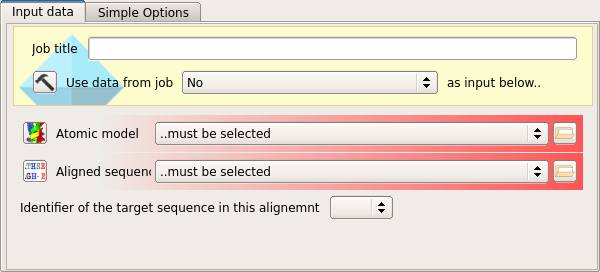
The task requires to data objects as input.
The first input is the atomic coordinates of the search model, as downloaded from the PDB.
The second input is a sequence alignment between the search model and the target structure.
Since the sequence alignment will contain two aligned sequences, the name of the target structure sequence in the alignment file must also be selected from the drop-down menu.
Options
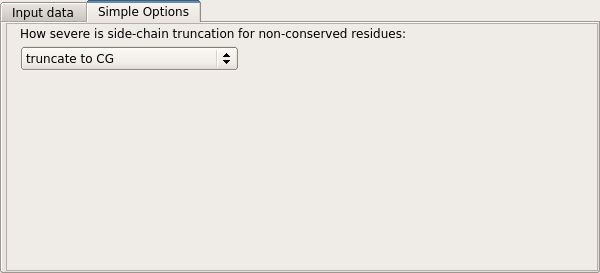
The level of truncation may also be selected. Currently, three modes are supported. The default, "truncate to CG", is the mixed model of Schwarzenbacher et al. in which non-conserved residues are truncated to the gamma atom, while conserved residues are preserved unchanged. The "truncate to CB" mode is similar, but non-conserved residues are truncated to the beta atom. The "tuncate to last common atom" mode retains the maximal number of atoms common to the target and model residues.
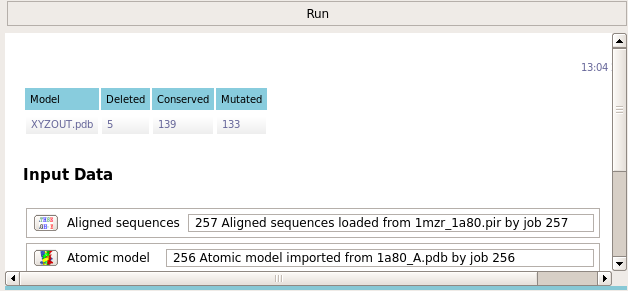
The task reports how many residues were conserved and how many were mutated.